In the previous blog of this series, we discussed 5G Advanced with respect to Release 18 which was completed in 2024. 5G Advanced will gradually mature across the Releases 18, 19 and 20 and ultimately lead to 6G. What will be the components and focus areas of 6G? Well, it is still at the nascent stage but if we consider the continuum of technology evolution and guiding framework of 6G – we can make some educated guesses.
From the guideline and standard perspectives, we have to consider two main standard bodies – ITU and 3GPP.
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is the United Nations specialized agency for Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs). They facilitate international connectivity in communication networks, allocate global radio spectrum and develop the technical standards that ensure networks and technologies connect seamlessly. Within the ITU, the ITU-R i.e., ITU Radiocommunication Sector plays a vital role in the global management of the radio-frequency spectrum and satellite orbits. ITU-R Working Party 5D (WP 5D) is responsible for the overall radio system aspects of the terrestrial component of International Mobile Telecommunications (IMT) systems, comprising the IMT-2000 (for 3G), IMT-Advanced (for 4G) and IMT-2020 (for 5G) as well as IMT-2030. This IMT-2030 is the 6G guidelines from ITU-R. 3GPP takes the responsibility of defining the detailed technical specifications that meet the requirements defined by the ITU. In this blog we mainly examine the IMT-2030 guidance.
User and Application Trends
9 user and application trends figure prominently in IMT 2030. These are mentioned below along with high level explanations:
Usage Scenarios and Overarching Aspects
Considering the above user and application trends, ITU has summarized the usage scenarios in 6 broad divisions as shown in the below diagram.

Immersive Communication, Hyper Reliable and Low Latency Communication, Massive Communication can be understood as extension of eMBB, mMTC and URLLC usage scenarios respectively. Ubiquitous Connectivity, AI and Communication, Integrated Sensing and Communication are new usage scenarios.
On top of these, 4 overarching design principles – Sustainability, Connecting the unconnected, Ubiquitous intelligence, Security and resilience are specified.
It may seem a lot of terminology but we can also get a sense of the 6G journey. It is gradually evolving towards a future with AI based distributed intelligence and pervasive connectivity.
Last but not the least, Tejas Networks has been playing an active role in shaping the 6G vision. Tejas Networks participated as part of the India delegation and contributed significantly to the ITU-R recommendation. The Indian delegation was instrumental in adding the Ubiquitous connectivity usage scenario into the wheel diagram. In the palette diagram, India helped to add Coverage and Interoperability as two additional capabilities. India also drove the effort to convert sustainability as one of the overarching aspects of 6G.
Stay tuned for knowing more about the exciting 6G research from Tejas in AI/ML, Network Energy Saving (NES), Sub-band Full Duplex (SBFD) etc.
References:
From the guideline and standard perspectives, we have to consider two main standard bodies – ITU and 3GPP.
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is the United Nations specialized agency for Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs). They facilitate international connectivity in communication networks, allocate global radio spectrum and develop the technical standards that ensure networks and technologies connect seamlessly. Within the ITU, the ITU-R i.e., ITU Radiocommunication Sector plays a vital role in the global management of the radio-frequency spectrum and satellite orbits. ITU-R Working Party 5D (WP 5D) is responsible for the overall radio system aspects of the terrestrial component of International Mobile Telecommunications (IMT) systems, comprising the IMT-2000 (for 3G), IMT-Advanced (for 4G) and IMT-2020 (for 5G) as well as IMT-2030. This IMT-2030 is the 6G guidelines from ITU-R. 3GPP takes the responsibility of defining the detailed technical specifications that meet the requirements defined by the ITU. In this blog we mainly examine the IMT-2030 guidance.
User and Application Trends
9 user and application trends figure prominently in IMT 2030. These are mentioned below along with high level explanations:
- Ubiquitous intelligence – 6G is expected to provide a lot more functionality beyond higher data speed. One such paradigm is ubiquitous intelligence i.e., AI based distributed intelligence across the network.
- Ubiquitous computing – it refers to generating intelligent environments, services, and applications utilizing ‘smart things’. Ubiquitous computing devices remain perpetually connected and accessible, leveraging the internet and wireless computing to provide the automated functionality.
- Immersive multimedia and multi-sensory interactions – Using digital technology that creates or enhances an environment, either to simulate the physical world or to create something completely new. Unlike traditional media, immersive media offers a more intense and interactive experience, engaging users on various sensory levels
- Integration of sensing and communication – Advanced sensing, precise positioning and low latency communication can help in multiple scenarios such as manufacturing, autonomous vehicle, warehouse management, mining and so on.
- Digital twin and virtual world – Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical systems, programed to behave identically to their original siblings. Digital twins open up a virtual world of possibility, it aids in network design/ optimization before doing actual change in the network.
- Smart industrial applications – Considering the above points, 6G can result in newer and diverse variety of industrial use cases such as precision agriculture, industrial automation, industrial IoT, reconfigurable intelligent services.
- Digital health and well-being – it include a plethora of services such as remote health monitoring, telemedicine, intelligent wearable devices etc.
- Ubiquitous connectivity – it means that data connectivity will be globally available even in challenging areas seamlessly.
- Sustainability – last but not the least, one of the key societal concerns is about sustainability and it is reflected in the 6G mandate as the need for more sustainable network operation.
Usage Scenarios and Overarching Aspects
Considering the above user and application trends, ITU has summarized the usage scenarios in 6 broad divisions as shown in the below diagram.
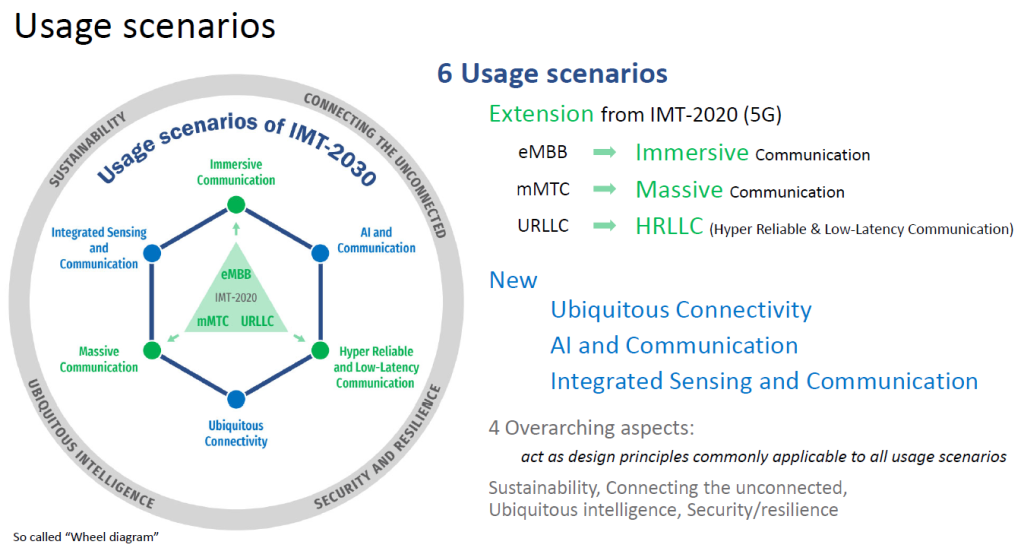
Figure 1: 6G Usage Scenarios Source: ITU-R
Immersive Communication, Hyper Reliable and Low Latency Communication, Massive Communication can be understood as extension of eMBB, mMTC and URLLC usage scenarios respectively. Ubiquitous Connectivity, AI and Communication, Integrated Sensing and Communication are new usage scenarios.
On top of these, 4 overarching design principles – Sustainability, Connecting the unconnected, Ubiquitous intelligence, Security and resilience are specified.
It may seem a lot of terminology but we can also get a sense of the 6G journey. It is gradually evolving towards a future with AI based distributed intelligence and pervasive connectivity.
Last but not the least, Tejas Networks has been playing an active role in shaping the 6G vision. Tejas Networks participated as part of the India delegation and contributed significantly to the ITU-R recommendation. The Indian delegation was instrumental in adding the Ubiquitous connectivity usage scenario into the wheel diagram. In the palette diagram, India helped to add Coverage and Interoperability as two additional capabilities. India also drove the effort to convert sustainability as one of the overarching aspects of 6G.
Stay tuned for knowing more about the exciting 6G research from Tejas in AI/ML, Network Energy Saving (NES), Sub-band Full Duplex (SBFD) etc.
References:
- https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-R/study-groups/rsg5/rwp5d/imt-2030/Pages/default.aspx
- https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-R/study-groups/rsg5/rwp5d/imt-2030/Documents/IMT-2030%20Framework_WP%205D%20Management%20Team_WEB%20POST%20v2_11-2023.pdf
- https://research.samsung.com/blog/All-set-for-6G
- https://oulurepo.oulu.fi/bitstream/handle/10024/36430/isbn978-952-62-2354-4.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
- https://www.itu.int/dms_pubrec/itu-r/rec/m/R-REC-M.2160-0-202311-I%21%21PDF-E.pdf


